Shipping Zones: Guide to Shipping Costs and Transit Times for Ecommerce
The concept of a shipping zone is important to grasp in the world of order fulfillment, yet many ecommerce business owners struggle to understand how zones work.
In this article, we’ll dive into some of the most common questions around shipping zones, so you can gain insight into the right shipping strategy for your online store. Let’s break it down!
So, what do you want to learn?
Request Fulfillment Pricing
We’ll get back to you within 24 hours. Privacy Policy
What are shipping zones?
Shipping zones are the geographical areas that carriers ship to, spanning from Zone 1 to Zone 8 for domestic shipments in the United States. Shipping carriers use shipping zones to measure the distance a package travels – not in miles but rather groupings of zip codes – from the point of origin to the destination.
How to calculate shipping zones
The location from which an order is shipped is the point of origin and located in Zone 1. The address it’s shipped to is the destination zone. The destination zone number will depend on how far it is from the point of origin, with Zone 8 being the farthest away.
Because zones are dynamically calculated based on where your package is shipped from, this could mean that two different points of origin that are shipping to the same destination address could be shipping to completely different zones.
For example, if you ship from Los Angeles, California to St. Louis, Missouri, you are shipping to Zone 7.
However, if you ship from Dallas, Texas to St. Louis, Missouri, you are shipping to Zone 4.
FedEx, UPS, USPS Shipping zones: what are they?
To estimate your shipping zones for USPS, UPS, and FedEx, use the table below (updated February 2022):
| Shipping Zone | Mile Radius (from origin) |
| Zone 1 (local) | 50 mile radius |
| Zone 2 | 51 – 150 mile radius |
| Zone 3 | 151 – 300 mile radius |
| Zone 4 | 301 – 600 mile radius |
| Zone 5 | 601 – 1000 mile radius |
| Zone 6 | 1001 – 1400 mile radius |
| Zone 7 | 1401 – 1800 mile radius |
| Zone 8 | 1801+ mile radius |
| Zone 9 | Freely Associated States |
Additional Resources:
- USPS Domestic Zone Chart: Navigate to the tab “Get Zone for ZIP Code Pair.” Simply enter the zip code you’re mailing from and the zip code you’re mailing to, and you will get the shipping zone for your destination.
UPS Zones and Rates for the 48 Contiguous States: Enter your zip code of origin and download zone charts to Excel.
How do shipping zones affect shipping costs?
Shipping costs for ecommerce parcels shipped within the US are determined based on two factors: the zone number to which you are shipping, and the weight of the parcel. Below, we break down each of these factors in more detail.
Zone number
Shipping carriers use zones to calculate rates for certain services, such as parcel shipments. For services that are zoned, the greater the zone, the greater the cost in most cases.
However, there are exceptions. Some carriers or services use a flat rate, letting you pay the same price regardless of the destination (as long as it’s within the United States).
For example, USPS breaks down which services are zoned (Priority Mail Express, Priority Mail, USPS Retail Ground, and Bound Printed Matter) and which are not (First-Class Mail, USPS Marketing Mail, Library Mail, and Media Mail).
Order Weight
Besides the carrier and service used, as well as the origin and destination zip codes, exact shipping rates will also depend on order weight and dimensions.
With the January 2019 change to zone-based pricing for even lightweight packages sent via USPS First Class Mail, all businesses are affected by distance. However, the heavier a package is, the more dramatic the price increase will be as the zones increase.
Let’s use the chart below as an example. If you are shipping a 1-pound package, the price increase from Zone 1 to Zone 10 is only $3.90. However, if you are shipping a 3-pound package, the price increase from Zone 1 to Zone 10 is $14.65.
Essentially, the amounts prices increase from zone to zone are smaller for lighter packages, while the amounts prices increase from zone to zone are larger for heavier packages.
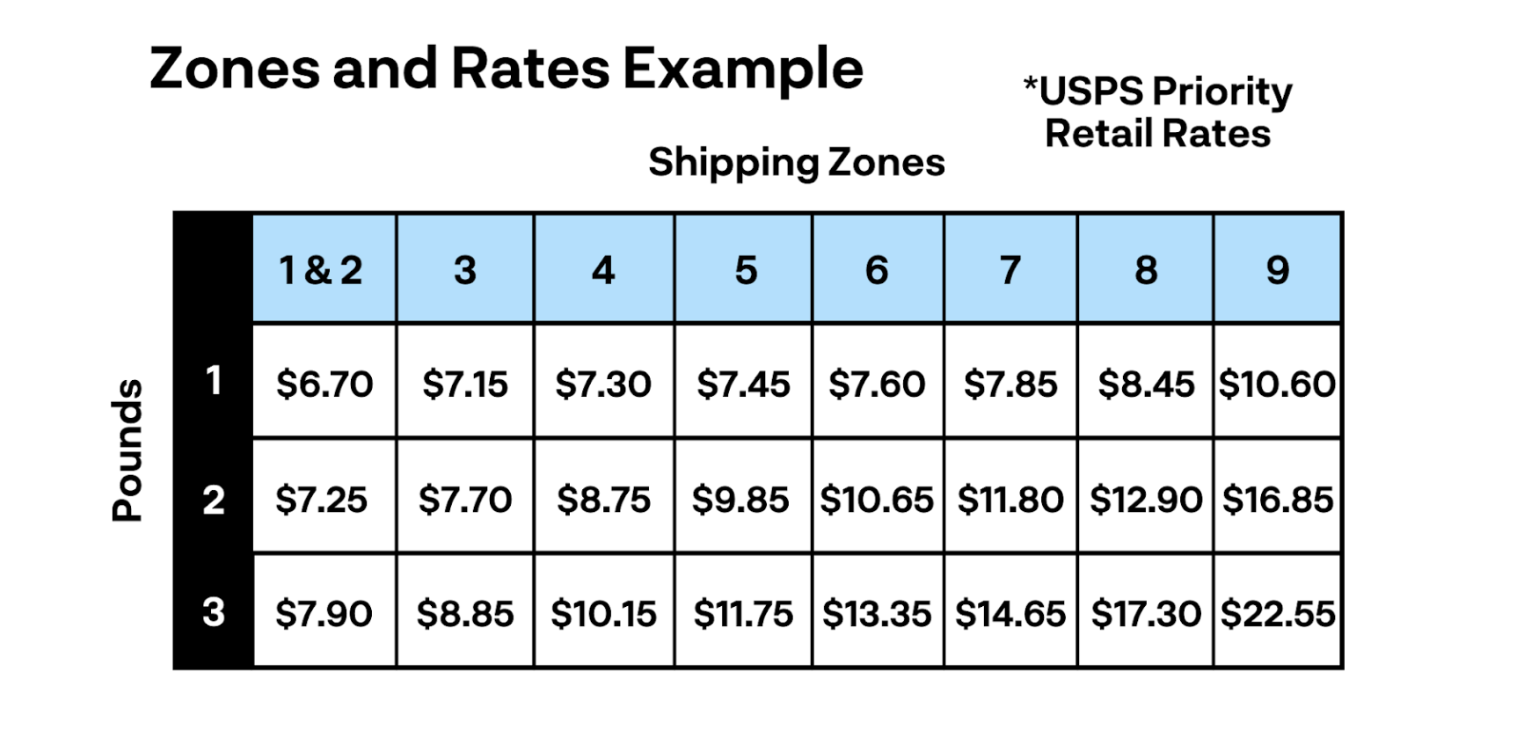
As this example demonstrates, both the shipping distance (measured by zones) and the order’s weight work together to impact the final shipping cost.
A note on dimensional weight: Shipping carriers use this pricing technique to estimate weight calculated from the length, width, and height of a package, using the longest point on each side. The shipping cost will be based on whichever number is greater: the actual weight of the package or its calculated dimensional weight.
How can ecommerce companies afford to offer free shipping?
It may seem counterintuitive to offer free shipping when it can be so expensive to send orders to high zones. Ecommerce companies that incorporate free shipping into their pricing strategy must be strategic in their decision to ensure it won’t hurt their margins. Typically, it’s done using one of the following options:
- They bake the cost of shipping into the product price (using the average shipping cost)
- They require a minimum dollar amount to be spent (to increase the average order value)
- They reduce the number of zones they ship to (more on that below)
How do shipping zones affect delivery speed?
If a package is sent nearby (e.g., Zone 1 or Zone 2), it will almost always arrive in fewer days than a package sent to a higher zone, like 7 or 8. Reducing time in transit is important, because slow shipping can cost you customers.
In fact, 73% of shoppers expect affordable, fast deliveries and 24% of customers cancel an order due to slow shipping.
[Related infographic: The State of Ecommerce: What You Should Know About Online Shoppers]
Customers today believe the maximum amount of time considered acceptable to wait for their order is only 4.1 days (as compared to 5.5 days back in 2012).
If all of your inventory is fulfilled from one location – for example, out of New Jersey, as seen in the map below – it can take 5-6 days to deliver an order to a customer in Oregon.
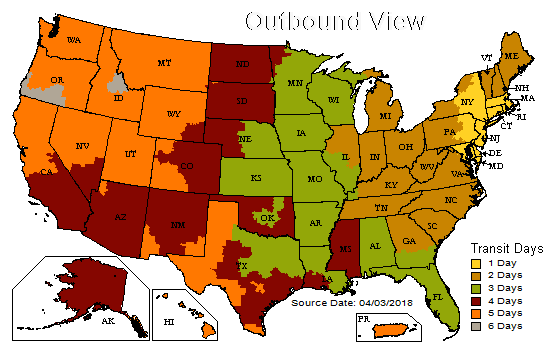
Therefore, it’s no surprise that same-day shipping and delivery can only ship to the lowest zone(s).
Reduce your shipping zones by distributing inventory
Since the higher shipping zones involve the highest shipping cost and transit time, is it possible to simply avoid shipping to the highest shipping zones?
It is possible — but to do it, you will need to be strategic about where you fulfill your orders from.
Where is the best place to fulfill orders to reduce shipping zones?
There isn’t one universal “best location” for fulfillment to reduce shipping zones; rather, the best location for your business are those that place your inventory closer to popular order destinations, as determined by analyzing your past order history. A facility close to a large city can help you reach a high volume of people faster, as opposed to shipping from a less densely populated area that can’t efficiently reach as many people.
Most of the time, though, an ecommerce business’s customers aren’t all in one city, or even one state, but are geographically dispersed across the country. To avoid being forced to ship to a high zone, many brands split inventory across multiple fulfillment centers that are located in different parts of the US.
Cost-savings
It may seem counterintuitive that using more fulfillment centers can save money, but there are many instances where it’s effective (most commonly by outsourcing fulfillment, as you won’t have leases, labor, equipment, and other expenses).
In the maps below, we compare the use of one fulfillment center in the continental United States with three fulfillment centers. The legend shows the color of each shipping zone, with red representing the closest and cheapest zone to ship to.
As the zones increase, the colors shift to orange, yellow, green, blue, and even purple.

When using one fulfillment center (in Moreno Valley California, as seen on the map to the left), we see one region of the country is shades of red and orange, yet much more is green, blue, and even purple — where the shipping rates will be higher, since it will go to Zone 8.
When using three fulfillment centers (in Moreno Valley, California; Dallas, Texas; and Bethlehem, Pennsylvania, as seen on the map to the right), there are many more red, orange, yellow, and green areas.
We’ve also eliminated the most expensive zones (Zones 7 and 8), leaving only a couple of areas that are in Zone 6. These three fulfillment center locations also provide coverage in highly populated states (e.g., California, Texas, and Pennsylvania), where the green areas are in many large states that have a small population (Montana, Wyoming, etc.).
Utilizing three fulfillment centers instead of one would enable more orders to be shipped to lower zones. In other words, the average shipping cost per order would dramatically decrease with the addition of each fulfillment center. Additionally, using multiple fulfillment centers can help you offer two-day shipping via ground in more regions, instead of relying on expensive air shipping.
[Related article: 3 Benefits of Using More Than One Fulfillment Center]
Ultimately, the distributed inventory approach can help you eliminate the most expensive shipping zones, lower its average shipping zone number, and save on shipping costs. Some brands have even seen that distributing inventory across several fulfillment centers can reduce fulfillment costs by $2/order and bring a 13% cost savings to their bottom line.
But before you commit to distributing your inventory, make sure you do the following:
- Analyze historical order and zip code data to reevaluate your optimal fulfillment locations.
- Determine if a more central warehouse location (or even a bi-coastal strategy) would benefit your business if you’re often shipping from one side of the country to the other.
- Calculate what your shipping costs would be if you went from one fulfillment center to two (or two to three, and so on) by experimenting with different locations, and how those would be offset by the additional transportation and warehousing costs you would incur.
Faster deliveries
In addition to reduced costs, distributing inventory also helps speed up transit times. While anybody can expedite shipments, the costs are very high, causing a major hit to margins and profitability. If you store inventory closer to customers, it can get to them faster via ground.
For example, the zone data below is based on ShipBob’s average standard US ground transit times (across all carriers), updated weekly from January 2020 through December 2021. It demonstrates timelines from click-to-delivery (i.e., when a customer places an order to when it is delivered to the shipping destination), broken out by shipping zones across the United States.
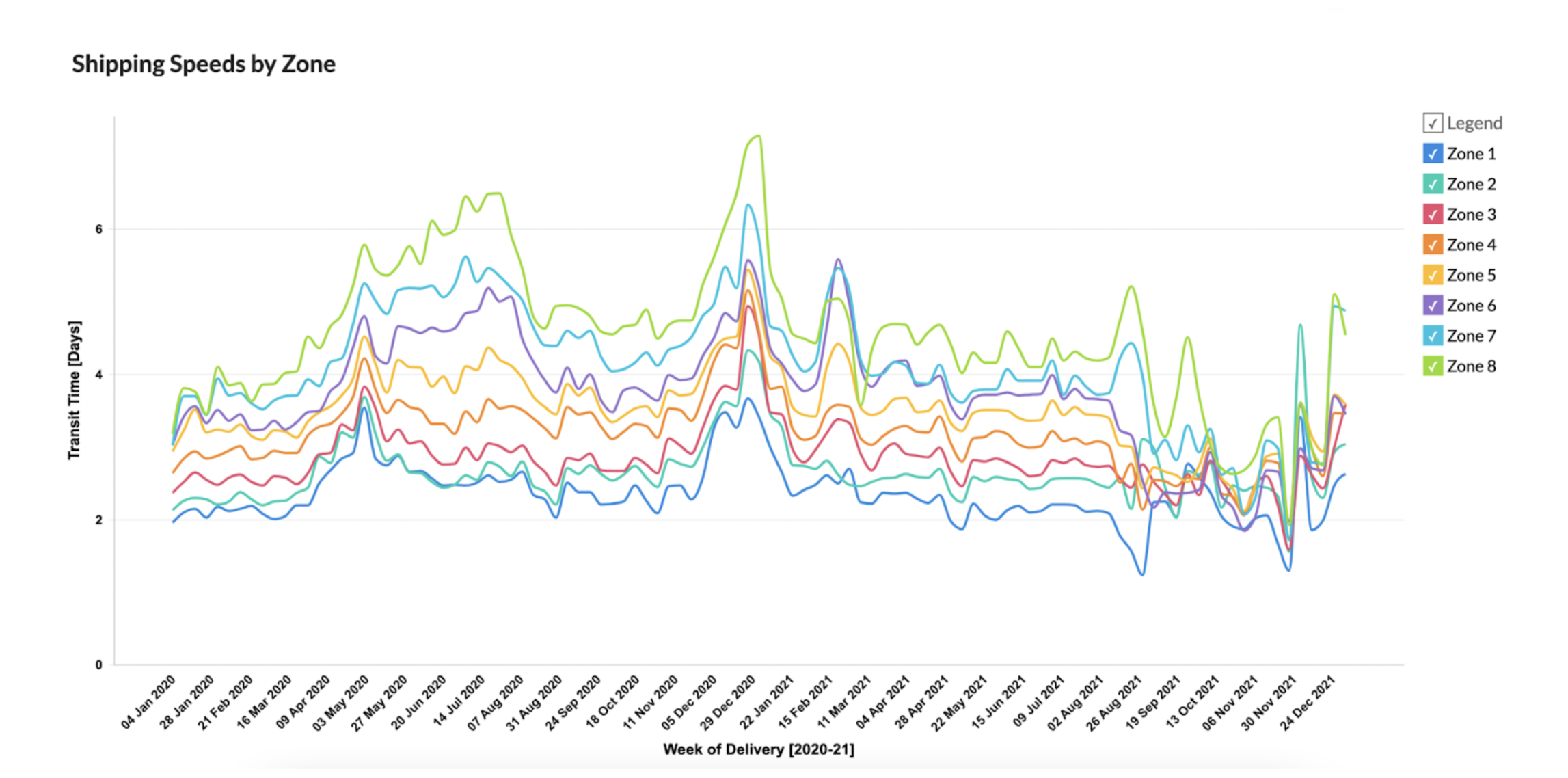
The top line (light green) represents the average Zone 8 shipment over time. Unsurprisingly, it is consistently the slowest zone to ship to, ranging from just over 3 days to 7.27 days at the very end of peak season 2020, just before 2021).
The bottom line (dark blue) represents the average Zone 1 shipment over time. The average for this more ‘local’ delivery ranged from 1.86 days to 3.66 days at the height of the 2020 holiday season.
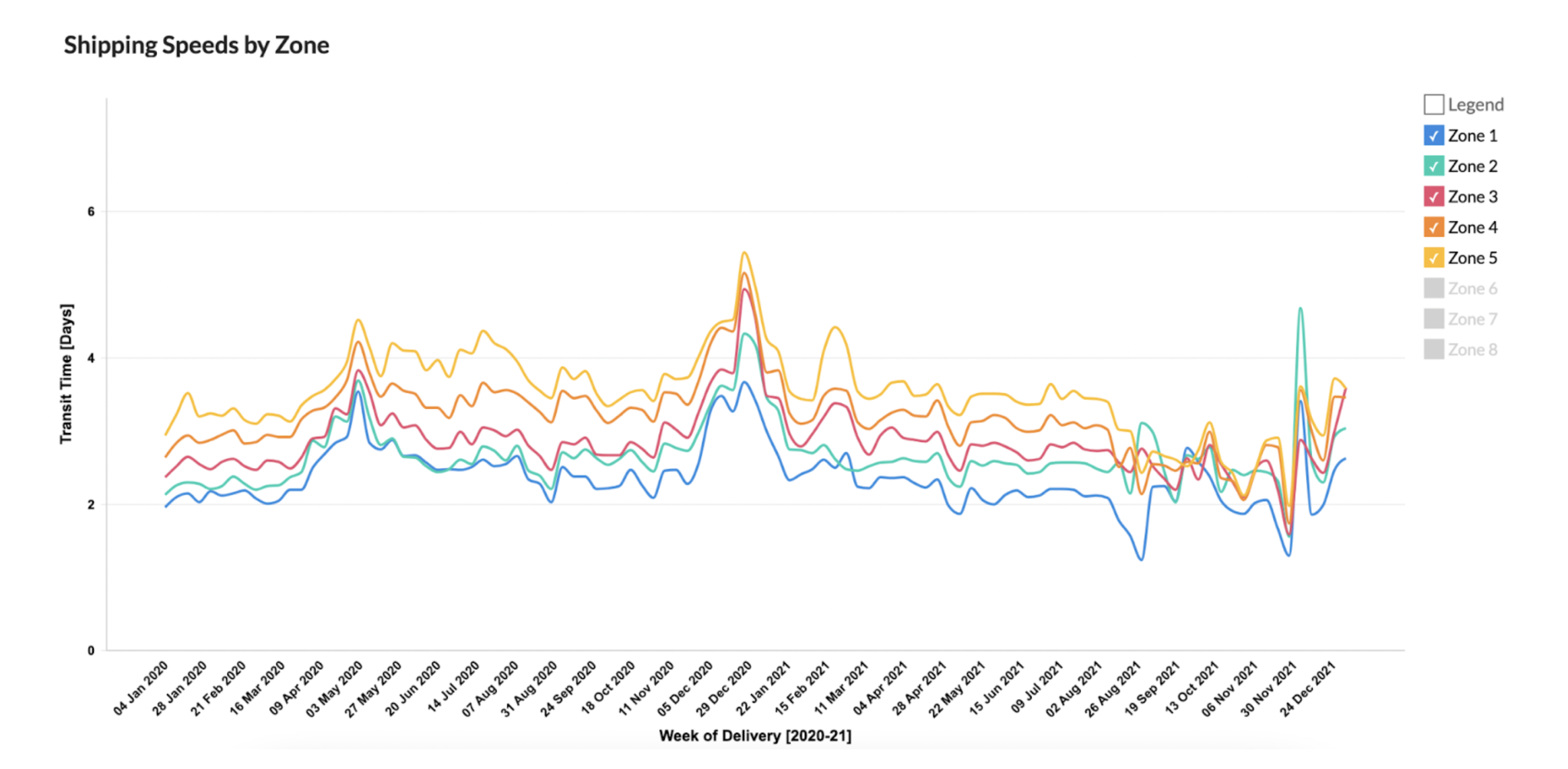
If we recall the map example, where we used 3 fulfillment centers across different regions of the US, we can eliminate the 3 highest zones (6-8) to see the updated shipping speeds below.
- For the highest zone remaining (Zone 5), the fastest average shipping speed was 1.97 days.
- The slowest average Zone 5 shipping speed was 5.43 days during the chaotic peak season of 2020 (which is a reduction of almost 2 days from the previous slowest Zone 8 shipping speed that same week).
4 ways to cut ecommerce shipping costs and transit times with a 3PL
As experts in the ecommerce and logistics industries, the best 3PLs can help your business implement best practices in your shipping strategy to navigate shipping zones, minimize costs, and maximize efficiency. Here are just a few of the benefits of partnering with a 3PL for your fulfillment and shipping.
Distribute inventory across a broad fulfillment network
The best 3PLs will have a number of fulfillment centers across the US — and even abroad — in which they store inventory and fulfill orders for their customers. This enables ecommerce business to reap all the benefits of distributed inventory (namely, cost savings and reduced transit times) without having to invest enormous amounts of capital they don’t have in establishing their own facilities.
Offers faster shipping times
Apart from the faster shipping times that distributing inventory provides, 3PLs can also shorten delivery times in other ways.
The right logistics partner will process and fulfill orders more efficiently than a business self-fulfilling its orders, which gets orders out for shipping faster and reduces lead time. Some 3Pls may even have expedited shipping programs available, so that ecommerce businesses can offer their customers 2-day shipping wherever they are.
Reduce shipping costs
In addition to lowering average shipping cost through distributed inventory, some 3PLs will also negotiate bulk shipping discounts with major carriers. Ecommerce businesses can then choose whether or not to pass the savings onto their customers.
Maintain higher customer satisfaction
Customers want fast shipping at an affordable price. By providing avenues to 2-day shipping and minimal shipping costs, 3PLs help ecommerce businesses satisfy shoppers’ expectations to build loyalty and win new business.
Conclusion
If you understand zone shipping, you can adjust your ecommerce fulfillment strategy to better meet customer expectations around speedy and affordable deliveries. Not only will this help you improve efficiency by reducing distance and time in transit, but it can also help you reduce shipping costs, generate more sales, and improve your bottom line.
To keep fulfillment costs and overall logistics costs down, you must effectively use zone shipping to your advantage. Learn how ShipBob helps ecommerce businesses do this by fulfilling orders from their network of fulfillment centers in the largest US cities to effectively reach customers.